What Role Does Vibration Play in Block Machine Performance?
Author:HAWEN Block MachineFROM:Brick Production Machine Manufacturer
TIME:2026-01-17
What Role Does Vibration Play in Block Machine Performance?
In modern concrete block production, vibration is not merely an auxiliary function—it is a core forming mechanism that directly determines product quality, production efficiency, and equipment reliability. A well-designed vibration system works in precise coordination with the hydraulic system to achieve optimal compaction, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. Understanding the role of vibration is therefore essential to evaluating overall block machine performance.
1. Vibration as a Compaction Mechanism
 The primary function of vibration in a block machine is to rearrange and densify concrete particles within the mold. When vibration is applied:
Aggregate particles overcome internal friction and interlock more efficiently
Cement paste flows uniformly, filling voids and encapsulating aggregates
Trapped air is expelled, reducing internal porosity
This process results in higher-density blocks with improved compressive strength and durability, while maintaining consistent geometry across production cycles.
2. Interaction Between Vibration and Hydraulic Pressure
High-performance block machines do not rely on vibration alone. Instead, vibration operates in synergy with hydraulic pressing:
Vibration mobilizes the material, reducing resistance to compaction
Hydraulic pressure applies controlled force to achieve final density
This combination allows the machine to reach target strength levels with lower peak pressure, minimizing stress on molds and structural components. The result is enhanced forming efficiency, reduced wear, and longer equipment service life.
The primary function of vibration in a block machine is to rearrange and densify concrete particles within the mold. When vibration is applied:
Aggregate particles overcome internal friction and interlock more efficiently
Cement paste flows uniformly, filling voids and encapsulating aggregates
Trapped air is expelled, reducing internal porosity
This process results in higher-density blocks with improved compressive strength and durability, while maintaining consistent geometry across production cycles.
2. Interaction Between Vibration and Hydraulic Pressure
High-performance block machines do not rely on vibration alone. Instead, vibration operates in synergy with hydraulic pressing:
Vibration mobilizes the material, reducing resistance to compaction
Hydraulic pressure applies controlled force to achieve final density
This combination allows the machine to reach target strength levels with lower peak pressure, minimizing stress on molds and structural components. The result is enhanced forming efficiency, reduced wear, and longer equipment service life.
 3. Influence on Surface Quality and Dimensional Accuracy
Properly controlled vibration has a direct impact on product appearance and precision:
Uniform vibration ensures even material distribution across the mold cavity
Controlled frequency and amplitude prevent segregation of aggregates
Stable vibration reduces edge defects, surface voids, and laminations
Consequently, blocks exhibit sharp edges, smooth surfaces, and tight dimensional tolerances, which are critical for structural integrity and downstream construction efficiency.
4. Vibration Parameters and Process Control
The effectiveness of vibration depends on accurate control of key parameters:
Frequency affects particle mobility and air release
Amplitude influences the depth and intensity of compaction
Duration determines the balance between densification and material stability
Advanced block machines allow these parameters to be adjusted according to raw materials, moisture content, and product type—whether hollow blocks, solid blocks, pavers, or curbstones. This adaptability ensures process consistency under varying production conditions.
3. Influence on Surface Quality and Dimensional Accuracy
Properly controlled vibration has a direct impact on product appearance and precision:
Uniform vibration ensures even material distribution across the mold cavity
Controlled frequency and amplitude prevent segregation of aggregates
Stable vibration reduces edge defects, surface voids, and laminations
Consequently, blocks exhibit sharp edges, smooth surfaces, and tight dimensional tolerances, which are critical for structural integrity and downstream construction efficiency.
4. Vibration Parameters and Process Control
The effectiveness of vibration depends on accurate control of key parameters:
Frequency affects particle mobility and air release
Amplitude influences the depth and intensity of compaction
Duration determines the balance between densification and material stability
Advanced block machines allow these parameters to be adjusted according to raw materials, moisture content, and product type—whether hollow blocks, solid blocks, pavers, or curbstones. This adaptability ensures process consistency under varying production conditions.
 5. Impact on Productivity and Energy Efficiency
An optimized vibration system contributes directly to operational efficiency:
Faster and more effective compaction shortens cycle times
Reduced rejection rates lower material waste
Lower required pressing force decreases overall energy consumption
From a production standpoint, vibration enhances throughput without compromising quality, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher output with controlled operating costs.
6. Equipment Reliability and Long-Term Performance
Balanced and well-engineered vibration systems protect the machine itself:
Even vibration distribution prevents localized stress concentrations
Reduced forming resistance lowers mechanical and hydraulic loads
Stable operation minimizes fatigue on frames, bearings, and molds
This translates into lower maintenance frequency, fewer unplanned stoppages, and greater long-term reliability.
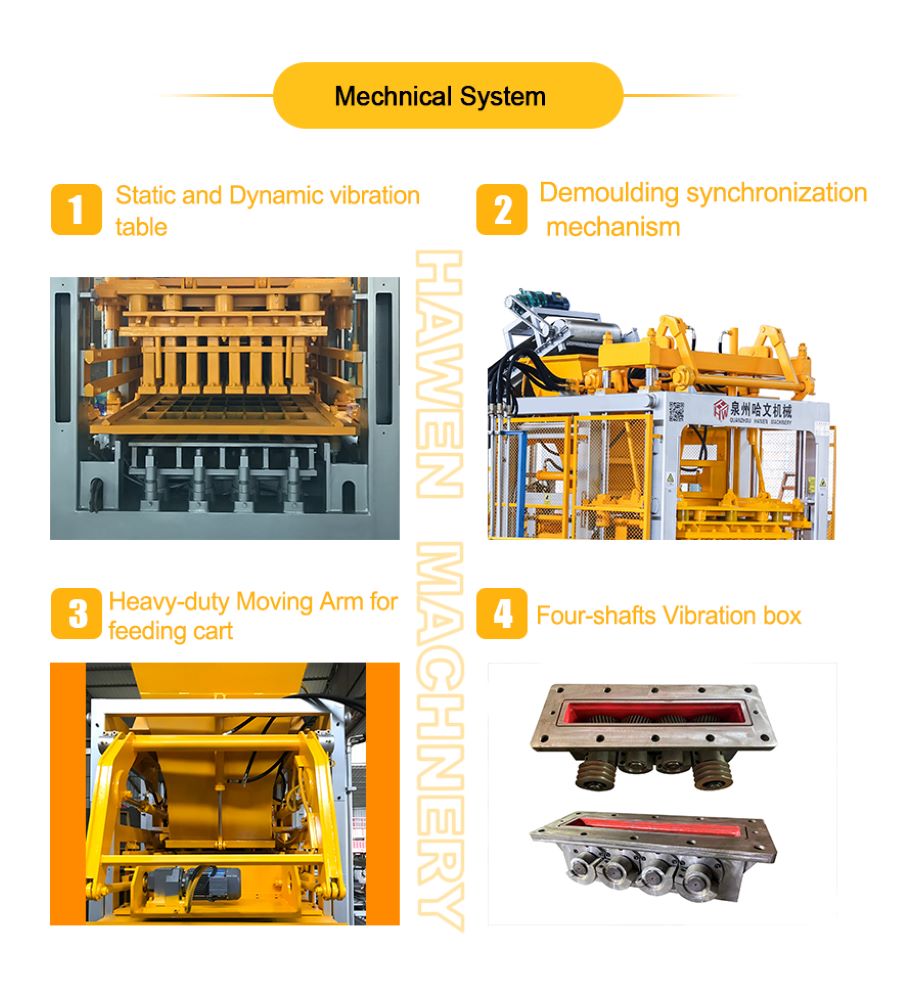
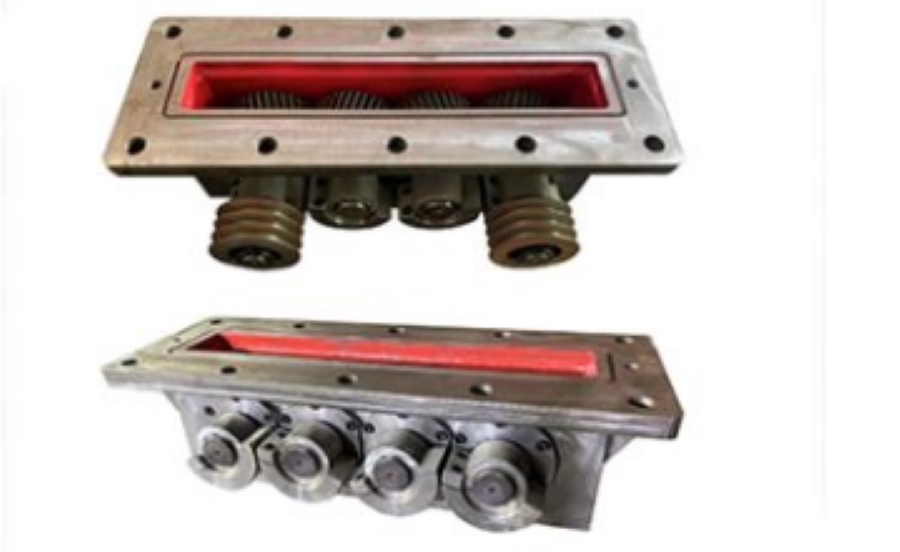
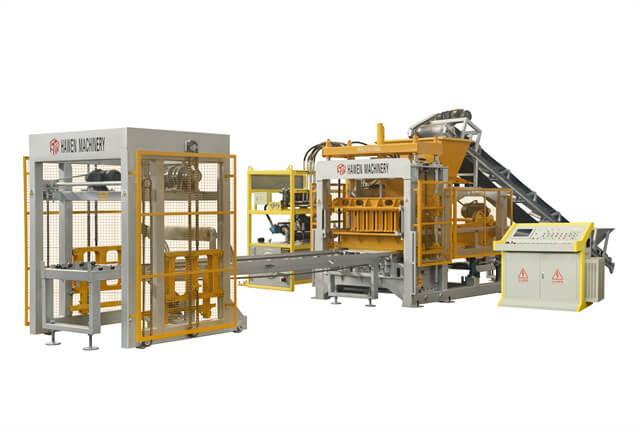
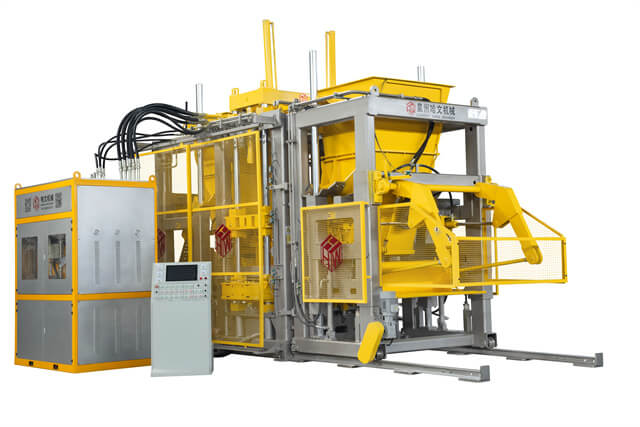
Four-Axis Vibration Box Design Advantage
Hawen Machinery adopts a four-Shaft vibration box design,In this configuration, the eccentric blocks are positioned outside the vibration box housing, resulting in significantly lower resistance during vibration.
So the oil temperature not easy to be increased even during long, continuous production cycles. This effectively reduces thermal impact on sealing components, minimizing wear and aging of sealing rings.
As a result, the four-axis vibration box design helps prevent oil leakage, improves operational stability, and significantly extends the service life of the vibration system, ensuring reliable long-term performance under high-load, high-output conditions.
5. Impact on Productivity and Energy Efficiency
An optimized vibration system contributes directly to operational efficiency:
Faster and more effective compaction shortens cycle times
Reduced rejection rates lower material waste
Lower required pressing force decreases overall energy consumption
From a production standpoint, vibration enhances throughput without compromising quality, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher output with controlled operating costs.
6. Equipment Reliability and Long-Term Performance
Balanced and well-engineered vibration systems protect the machine itself:
Even vibration distribution prevents localized stress concentrations
Reduced forming resistance lowers mechanical and hydraulic loads
Stable operation minimizes fatigue on frames, bearings, and molds
This translates into lower maintenance frequency, fewer unplanned stoppages, and greater long-term reliability.
Four-Axis Vibration Box Design Advantage
Hawen Machinery adopts a four-Shaft vibration box design,In this configuration, the eccentric blocks are positioned outside the vibration box housing, resulting in significantly lower resistance during vibration.
So the oil temperature not easy to be increased even during long, continuous production cycles. This effectively reduces thermal impact on sealing components, minimizing wear and aging of sealing rings.
As a result, the four-axis vibration box design helps prevent oil leakage, improves operational stability, and significantly extends the service life of the vibration system, ensuring reliable long-term performance under high-load, high-output conditions.
 Conclusion
Vibration plays a decisive role in block machine performance by directly influencing compaction efficiency, product quality, production speed, and equipment durability. When precisely engineered and intelligently controlled, vibration transforms raw materials into high-strength, dimensionally accurate blocks with optimal energy utilization. In modern block manufacturing, effective vibration is not an option—it is a fundamental requirement for consistent, high-performance production.
Conclusion
Vibration plays a decisive role in block machine performance by directly influencing compaction efficiency, product quality, production speed, and equipment durability. When precisely engineered and intelligently controlled, vibration transforms raw materials into high-strength, dimensionally accurate blocks with optimal energy utilization. In modern block manufacturing, effective vibration is not an option—it is a fundamental requirement for consistent, high-performance production.


















 Tel: +86-13905968794
Tel: +86-13905968794 Email: export@hwmachines.com
Email: export@hwmachines.com MP/WhatsApp: +86-13905968794
MP/WhatsApp: +86-13905968794 Manufacturer Address:Nanan,Quanzhou City,Fujian Province,China
Manufacturer Address:Nanan,Quanzhou City,Fujian Province,China